 |
 |
Class represents clustering algorithm X-Means. More...
Public Member Functions | |
| def | __init__ (self, data, initial_centers=None, kmax=20, tolerance=0.025, criterion=splitting_type.BAYESIAN_INFORMATION_CRITERION, ccore=True) |
| Constructor of clustering algorithm X-Means. More... | |
| def | process (self) |
| Performs cluster analysis in line with rules of X-Means algorithm. More... | |
| def | get_clusters (self) |
| Returns list of allocated clusters, each cluster contains indexes of objects in list of data. More... | |
| def | get_centers (self) |
| Returns list of centers for allocated clusters. More... | |
| def | get_cluster_encoding (self) |
| Returns clustering result representation type that indicate how clusters are encoded. More... | |
Class represents clustering algorithm X-Means.
X-means clustering method starts with the assumption of having a minimum number of clusters, and then dynamically increases them. X-means uses specified splitting criterion to control the process of splitting clusters. Method K-Means++ can be used for calculation of initial centers.
CCORE option can be used to use the pyclustering core - C/C++ shared library for processing that significantly increases performance.
CCORE implementation of the algorithm uses thread pool to parallelize the clustering process.
Here example how to perform cluster analysis using X-Means algorithm:
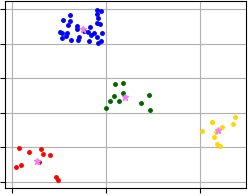
Visualization of clustering results that were obtained using code above and where X-Means algorithm allocates four clusters.
| def pyclustering.cluster.xmeans.xmeans.__init__ | ( | self, | |
| data, | |||
initial_centers = None, |
|||
kmax = 20, |
|||
tolerance = 0.025, |
|||
criterion = splitting_type.BAYESIAN_INFORMATION_CRITERION, |
|||
ccore = True |
|||
| ) |
Constructor of clustering algorithm X-Means.
| [in] | data | (list): Input data that is presented as list of points (objects), each point should be represented by list or tuple. |
| [in] | initial_centers | (list): Initial coordinates of centers of clusters that are represented by list: [center1, center2, ...], if it is not specified then X-Means starts from the random center. |
| [in] | kmax | (uint): Maximum number of clusters that can be allocated. |
| [in] | tolerance | (double): Stop condition for each iteration: if maximum value of change of centers of clusters is less than tolerance than algorithm will stop processing. |
| [in] | criterion | (splitting_type): Type of splitting creation. |
| [in] | ccore | (bool): Defines should be CCORE (C++ pyclustering library) used instead of Python code or not. |
| def pyclustering.cluster.xmeans.xmeans.get_centers | ( | self | ) |
Returns list of centers for allocated clusters.
| def pyclustering.cluster.xmeans.xmeans.get_cluster_encoding | ( | self | ) |
Returns clustering result representation type that indicate how clusters are encoded.
| def pyclustering.cluster.xmeans.xmeans.get_clusters | ( | self | ) |
Returns list of allocated clusters, each cluster contains indexes of objects in list of data.
Definition at line 190 of file xmeans.py.
Referenced by pyclustering.samples.answer_reader.get_cluster_lengths().
| def pyclustering.cluster.xmeans.xmeans.process | ( | self | ) |
Performs cluster analysis in line with rules of X-Means algorithm.